Trifecta Month for GTS; NYSE DMM, Quant-Trading Powerhouse and Fin-Tech Think-Tank Now Aligned With Investment Bank Specializing in Primary Debt & Equity Capital Markets
GTS, the NYSE’s Top DMM, and one of the global trading market’s leading multi-asset electronic market-makers, is on a strategic deal-making binge. On the heels of GTS co-founder and CEO Ari Rubenstein’s November 2 announcement that his firm acquired Cantor Fitzgerald’s 35-member ETF market-making and institutional broking crew, last Thursday while in London, Rubenstein announced that GTS is expanding its collaboration with BNP Paribas to now include live-streaming US equities pricing, on top of already delivering GTS’s UST price feed through BNP’s platform. Making November a hat-trick month for GTS, Rubenstein today announced that his firm is joining forces with boutique investment bank Mischler Financial Group (“Mischler”), a specialist in primary debt and equity capital markets and institutional brokerage providing secondary market execution for equities and fixed income.
Founded in 1994, Mischler Financial is also the industry’s oldest diversity firm owned and operated by service-disabled veterans; a designation that enables GTS to advance a Diversity & Inclusion (D&I) value-add to its armory of new solutions and client experience that GTS will bring to investment managers and issuers of debt and equity across the listed-company landscape.
Below is the opening extract of the press release.
New York, NY – November 19, 2018 – GTS, the New York Stock Exchange’s largest Designated Market-Maker (“DMM”) and a leading electronic trading firm, and Mischler Financial Group, Inc. (“Mischler”), the financial services industry’s oldest minority broker-dealer owned and operated by service-disabled veterans, today announced a strategic alliance that will establish a best-in-class offering for primary debt and equity market underwriting as well as secondary market best execution across the capital markets.
The partnership, which is anchored by a technology-powered offering for public companies and a broad universe of capital markets participants, will yield a low-cost, more efficient and more effective trade execution experience. Mischler will become a “forward operating base” for the growing GTS capital markets franchise, affording clients access to technology and sources of liquidity that are generally only available to the world’s most sophisticated investors.
Founded in 2006 as a proprietary, quantitative trading firm, GTS is now a recognized thought-leader in market structure and proudly oversees trading for more than one-third of NYSE-listed companies. The firm has an extensive track record developing and deploying proprietary, industry-best technology to bring better price discovery, trade execution and transparency to the markets.
“This is a high-tech, high-touch partnership designed to meet the needs of a new generation of issuers, asset managers, and trading and investment professionals seeking low-impact market liquidity and best-in-class execution,” said Ari Rubenstein, Co-Founder and Chief Executive Officer of GTS. “Clients are rightfully demanding innovation in the marketplace, and this alliance is uniquely designed to provide that and much more.”
Mischler, established in 1994, is an active underwriter across global equities, corporate and municipal debt, government securities and structured products. In the last three years alone, Mischler has played a role in almost 700 primary debt and equity market transactions. The firm also provides conflict-free share repurchase services for corporate treasurers as well as secondary market trade execution in equities and fixed income for a discrete universe of public plan sponsors and institutional investment managers.
Continue to the entire news announcement here
If you’ve got a hot insider tip, a bright idea, or if you’d like to get visibility for your brand through MarketsMuse via subliminal content marketing, advertorial, blatant shout-out, spotlight article, news release etc., please reach out to our Senior Editor via cmo@marketsmuse.com



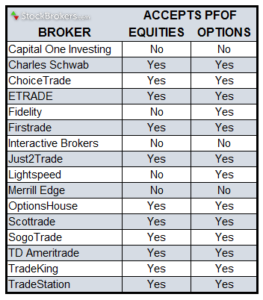 Here’s the excerpt from WSJ reporting by Cezary Podkul:
Here’s the excerpt from WSJ reporting by Cezary Podkul:










 Excerpt courtesy of April 15 edition of WSJ and reporters Scott Patterson and Andrew Ackerman.
Excerpt courtesy of April 15 edition of WSJ and reporters Scott Patterson and Andrew Ackerman.