Stock Price Implosion Leads Some to Challenge Current Market Structure; HFT Firms Are Under Attack, Again…
Heads Up to High-Frequency Firms: Time to Hire a PR Crisis Manager Again, Call Your Lobbyists, Book Your Plane Tickets to Washington DC.
Before “bidding on” to the anti-HFT and anti-ETF remarks circulated by the assortment of market pundits appearing on Bloomberg, Reuters or the financial media megaphone channel, CNBC, you should know that SecTres Mnunchin has already weighed in. So has the SEC’s favorite tech entrepreneur, Mark Cuban. So has icon stock investor Leon Cooperman, who has the ear of Mnuchin and others. There’s a whole ‘hang-em-high’ crowd assembling to lay blame on high-frequency trading for the latest market routs. According to CNBC, Trump favorite Mike Flynn was overheard shouting to Mnuchin and Trump: “Lock them up!”

But, unless you’ve been investing in or trading in the equities markets for at least 20 years, you probably have no conception of a simple premise: markets go up and markets go down. Blame games are easy to play, equities investing is not always easy.
Traditional drivers to stock price movements include simple, time-tested fundamentals: the interest rate environment, the economic cycle, the value of the US dollar vs. other currencies, corporate revenue and profit, corporate debt levels, consumer debt levels, trends in residential real estate prices and other consumer optimism metrics. Yes, you can throw in the degree of confidence in the current government administration and a bunch of other geopolitical stuff (including tariff wars, Brexit event, and total uncertainty in many countries’ leadership–including the US) into the mix. We’ve all grown accustomed to the minute-to-minute chaos caused by the current president. His impact on stock prices is powered by his Twitter comments about China, the Federal Reserve Chairman, and blaming the latest government shutdown on democrats. Beyond that, institutional investors can only make investment decisions based on reality within context of company earnings reports and not easily-fudged economic data. Investors should NOT make decisions based on a reality TV show produced in Foggy Bottom.
But, we should agree on one thing: the combination of complacent investing, a belief that prices of company shares will go up year after year is a fool’s view. The topic of debate in this post is whether the evolution of high-frequency trading (aka HFT) weaponry has contributed (yet again) to the large (downward) percentage moves in stock prices during the recent weeks. The sell-off, which arguably began during the first week of October, has led to an approximate 20% decline in the leading stock indices from the record highs. Many individual share prices have suffered bigger mark-downs, most notably tech sector stocks. Before asserting that high-frequency trading algorithms are the culprit, one need to ponder whether those same HFT tools also contributed to the nearly 50% gains the stock market has enjoyed since the 2016 US presidential election (two years ago)?
Whatever black swans have been flying over head for the past 6 months, now that equity prices have suffered multiple-day declines of 1%-3% (and the interim 1%-2% “dead cat bounce”) we need to blame someone!! After all, our very own president has been unwavering in his leadership mantra: “When the shit hits the fan, blame someone else for the problem!”
Let’s say you want to blame HFT firms for the slide. Considering the fact that today, the 3 largest NYSE market-makers are better known

for their legacy as high-frequency trading outfits, its easy to be cynical. These are ‘not your father’s NYSE specialist firm’, these are young quant jocks who made a ton of money as HFT prop trading shops starting back in the early 2000’s, and more recently, used some of that cash to purchase the legacy NYSE market-maker firms; the firms responsible for maintaining fair and orderly markets in NYSE listed companies. Now known as NYSE “DMMs”, they (actually their computers) also have the “first look” at orders to trade shares in which they are now the designated market-maker for. Instead of old-fashioned auction markets, these folks utilize algorithmic trading tools to match buyers and sellers and also trade for themselves. As a consequence, there is circumstantial evidence these firms are, to some extent, culpable for the rapid reflex moves in share prices.
Keep in mind, the flip-side is that these ‘HFT black boxes’ are also providing instantaneous liquidity, price transparency, and facilitate exiting or entering a investment position in less time than it takes to hit a ‘send’ button (until someone unplugs the machine after realizing they’ve risked the entire firm’s capital). Further, because everything happens in nano-seconds, one can argue that bear market cycles –periods that typically reflect recessionary pressures and in turn, signals that lead to a negative impact on the value of a company’s equity shares—are now much shorter in duration when compared to cycles going back 60-70 years.
To the first question, who can forget the May 2010 ‘Flash Crash’—an event that was certainly connected to HFT computers plugged into the walls surrounding the NYSE and NASDAQ computer server farms–and then became unplugged by humans when markets cratered due to a “fat finger” episode. We’ll tell you who cannot remember that event (other than having read about it years later): upwards of 1/3 of current ‘senior’ Wall Street quant jock HFT programmers who code the HFT machinery. Many of them were mining bitcoins in their MIT dorm rooms back in 2010. How many of the current generation of ‘systematic traders’ who now oversee billions of dollars were beyond high school in 2004? How many current trading desk wonks were around during the dot com bubble? How many folks who worked on trading desks in 1987 are even still alive, no less working in the business? Have you gotten the point, yet?
Because our pundits have accurately predicted this latest market down draft, allow us to further predict that we want to be “long on” private jet services to Washington (NYSE: BRK.A) and we’d love to invest in engagement contracts issued by PR Crisis Management gurus who represent these folks; they are presumably getting calls already by the best-known HFT honchos, starting yesterday.
Let’s be clear, the fundamental economic underpinnings that power equity prices have been sending mixed (warning) signals for months. OK, employment figures have been good, but Trump told us while campaigning for president that “US Employment figures are fake and fraudulent.” Yes, corporate earnings have met expectations, but nobody has delivered out-sized reports, and many companies have been sweating to provide realistic expectations, not wild-ass projections. According to recent polls, nearly 50% of Fortune CFOs are anticipating a recession will hit the US economy in 2019. 80% of CFOs believe a recession will be upon us before the end of 2020. Many multi-nationals based in the US are lamenting “Tariff Man” tweets. He says ‘US companies with US employees that make/sell products to US consumers will benefit, and the big companies have plenty of money to cushion the blows..” Really?!
So, fundamentals have been weakening during the past 2 quarters (unemployment figures aside). Even for those who subscribe to technical analysis and historic charts, the writing has been on the wall for months: “Caution Mr. Robinson, Caution!”
High-flying tech company shares started cracking in the 2nd quarter of 2018. They’ve been under an assortment of pressures that range from severe government and shareholder scrutiny to simple supply/demand obstacles impacting their business models (e.g. FB down nearly 40%, GOOG down 30% from its high, AAPL down 40%, AMZN down etc etc.) Bank stocks have been pummeled for the most part, even if GS’s latest beating is connected to yet another multi-billion dollar scandal. Big ticket corporate acquisitions made in the past 2 years have resulted in transition management problems. Corporate balance sheets have become increasingly overly-bloated with debt, thanks to folks on Wall Street who came up with a new pitch to corporate treasurers starting back in 2011: “We’ll float your bond offering (and get a big fee), you use the proceeds to repurchase outstanding shares, and you’ll make your EPS numbers look fantastic; everyone wins!!” Until the music stops, of course. Corporate share repurchases have been credited with keeping equity prices stable and moving higher for upwards of seven years; the brokers are making nice commission on executing those buybacks and all is good with the world, until its not.
Stock market chartists started raising red flags in October. Corporate debt issuance came to a crashing stop in the last 6-8 weeks. That was a big signal. Less than two dozen Fortune companies have actually been buying back debt in the past quarter in preparation for the next shoe to drop; the one with the word ‘recession’ stamped on the bottom of each shoe. The notion that corporations should unwind the ‘sell debt, buy shares’ trade –by issuing new shares and using the proceeds to balance the balance sheet and repurchase outstanding debt is an idea that no investment bank would even suggest in his sleep, no less in an office. It would be professional suicide for a corporate CFO to even suggest that idea makes sense. Geopolitical impact re Trump’s tariff war is hitting US companies and US workers, even if not the Trump Hotel enterprise. The corporate tax cut was a short shot of heroin that stimulated the stock market, but increased the Federal deficit by nearly $1trillion. (Let’s not forget that Trump campaigned on reducing debt, not increasing it–but so does every other candidate). Now people are coming off the sugar high and that’s how/why stock prices revert to the mean.
Tariff Wars, Brexit and the assortment of geopolitical catastrophes have all been thrown into the mixing bowl. Crude oil prices have been crushed–along with the share prices of companies that drill, process and sell oil-based products. Yes, we’ll repeat: employment figures have been great, but as Donald Trump said throughout his presidential campaign, “Nobody can believe government employment figures, they’re all fake news!”
When weighing the assortment of fundamental signals that have been brightly broadcast throughout the past 9-12 months—and certainly since October of this year, anyone who had not re-balanced or pared down exposure to equities has no business investing in stocks. Its easy to say “Ok, 20-20 hindsight is great..blah blah blah..” For those following @marketsmuse, there’s no 20-20 hindsight; our resident pundits (with trading market pedigrees that go back to the 1980’s) have been shouting “Caution Ahead!!” for at least 4 months. (see the pinned tweet). But, who wants to listen to experienced (if not cynical) professionals who have lived through multiple market cycles, especially when prices keep going up? Who wants to risk taking a profit and paying taxes on those gains when the asset value keeps going up, with or without fundamental justification? The answer: people who are (i) naïve (ii) overly-optimistic (iii) financially irresponsible (iv) not old enough to appreciate that what goes up, must go down.
Whatever black swans have been flying over head for the past 6 months, now that equity prices have suffered multiple-day declines of 1%-3% (and the interim 1%-2% “dead cat bounce”) we need to blame someone!! After all, our very own president has been unwavering in his leadership mantra: “When the shit hits the fan, blame someone else for the problem!”
Before the ink was dry on the famous Michael Lewis book “Flash Boys,” which profiled the May 2010 stock market crash, everyone knew who to blame. Before the first 1000 copies of that book left Barnes & Noble, government officials and regulators were busy sending out outlook meeting invites to the primary suspects-the heads of HFT proprietary trading firms that had come to dominate the trading of shares in US companies listed on public exchanges (and ‘dark venues), as well as stock index futures traded on electronic venues in Chicago.
Rules were introduced. Market structure lobbying groups were formed. Exchange executives pilot tested uptick rule changes. Fintech firms that provided ‘better solutions’ now represent more than just a cottage industry as evidenced by the fact, three of the leading HFT firms have through acquisition, become the three largest NYSE DMMs. For old folks, DMM is the contemporary phrase for ‘floor specialist’-the folks who are responsible for maintaining fair and orderly markets in the companies the NYSE assigns to market-makers on the floor of the NYSE. Pay-to-play and maker-taker rebate schemes advanced by brokers and exchange venues have flourished. Blah Blah Blah. Along the way, the US equities market, spurred by improving economic circumstances, and the last 10 years have been pretty much one long wet dream for traders and stock investors. The evolution of high-frequency trading morphed even more.
Irrespective of bull vs. bear views on individual stocks and stock indices and the 1500+ Exchange-Traded Funds that provide thematic investing styles, more than a carload of institutional investment managers still agree on one simple fact: share price movements in individual companies and ETFs are exacerbated by high-powered black boxes that spit out millions of orders per minute. Those orders are often based on what has transpired in the markets during the past few seconds. This algorithmic approach to trading causes educated investors to scratch their heads when observing the value of shares in public companies can gyrate so violently in the course of an hour or a day, despite the fact those companies haven’t made any earnings report nor announced any positive or negative news as to the health of their business or the industry they sit in.
How does a company’s enterprise value move 10% down one day, then 5% up the next? Are there so many investors with differing views who are expressing these views constantly via buying and selling millions of shares? No. Honest electronic trading industry experts will estimate that at least 80% of the time, transactions taking place at the NYSE or NASDAQ are between two ‘transformers’; computer bots that are set on auto-trade. These black box powered bots do not represent investors, they don’t smoke (unless the computer is overheated and not residing in a freezer), they don’t curse and they don’t sweat—they simply spit out–orders based on algorithms.
Put more simply, actual investors are not involved in upwards of 90% of the trades taking place. Bottom line: the exaggerated changes in publicly traded corporate enterprise values that take place from second to second are even more pronounced as prices move lower. That’s a real fact, not a Kelly Ann Conway or Sarah Huckabee-style “alternative fact.” More than a handful of objective market observers and participants have long argued that Wall Street has evolved into a Battle of the Transformers”; price moves and volatility are powered by computers, not by momentary sentiment changes on the part of real investors.
But, we live in a blame game world, as best evidenced by our so-called leaders (yes, we’re referring to the current occupant of the White House) who, when faced with obstacles or after making stupid decisions, automatically blame others for the disaster that occurred recently. And those blames are applauded by the blind mice and sheep who go along with the stupid decisions made for them.
Because our pundits have accurately predicted this latest market down draft, allow us to further predict that we want to be “long on” private jet services to Washington (NYSE: BRK.A) and we’d love to invest in engagement contracts issued by Wall Street-friendly PR Crisis Management guru. Those folks will be on speed dial for the best-known HFT honchos, starting yesterday. Caveat Emptor: PR crisis management should be advanced by smart folks, not those trained in the art of jibber jabber and deflection. If there is a fundamental flaw, acknowledge it and implement transparent steps that will appease the plaintiffs and provide real solutions to the ‘problem’ .
If you’ve got a hot insider tip, a bright idea, or if you’d like to get visibility for your brand through MarketsMuse via subliminal content marketing, advertorial, blatant shout-out, spotlight article, news release etc., please reach out to our Senior Editor via cmo@marketsmuse.com



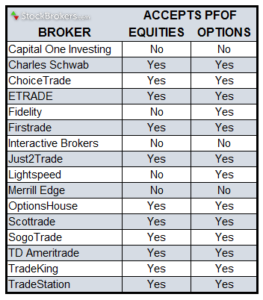 Here’s the excerpt from WSJ reporting by Cezary Podkul:
Here’s the excerpt from WSJ reporting by Cezary Podkul:










 Excerpt courtesy of April 15 edition of WSJ and reporters Scott Patterson and Andrew Ackerman.
Excerpt courtesy of April 15 edition of WSJ and reporters Scott Patterson and Andrew Ackerman.