MarketsMuse Global Macro and Fixed Income desks converge to share extract from 23 July edition of Rareview Macro commentary via its newsletter “Sight Beyond Sight”. For those not following the corporate bond market, most experts will tell you the equities markets follow the bond market–which in turn is a historical indicator when it comes to economic expansion, contraction, and recession. Below is courtesy of Rareview’s founder/managing member Neil Azous .
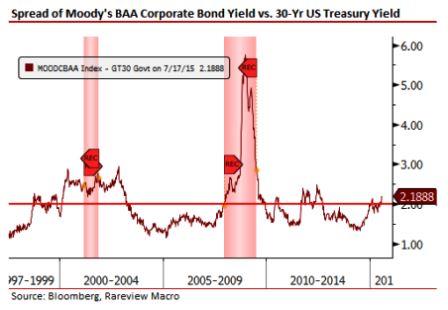
In the past few days, US investment grade (IG) credit spreads have reached new three year wides. Historically, the absolute level of these spreads is consistent with periods of economic and financial market stress. Additionally, the daily volatility of these spreads has increased dramatically in recent weeks.
Below is a chart of the Moody’s Baa Corporate Bond yield spread over the US 30-year Treasury yield.
What is the significance of this observation?
Investment grade corporate bonds are one of the least risky investments within the capital structure, and less sensitive to changes in default risk due to economic weakness. Moreover, the credit market is arguably, next to the slope of the yield curve, the greatest predictor of future economic stress.
The most widely cited explanation for the recent widening in spreads is that it is due to the amount of new investment grade credit issuance. Indeed, that is one factor as new issuance (+SSA) set a record pace yesterday after having surpassed $1 trillion, a level not reached last year until mid-September.
However, the recent widening of the spreads is not just down to the recent surge in corporate issuance. Issuance is simply not a large enough driving force to cause this level of “stress”. The reasons for this widening are two-fold.
Firstly, the aggregate level of issuance, to a degree, is beginning to finally catch up with the market after years of sensational appetite. Corporations, in aggregate, are raising their leverage levels by issuing the new debt and not using the proceeds to grow their revenues or cash flows to compensate. Put another way, the market is beginning to segregate between issuance related to refinancing a company’s “credit stack” as part of its normal annualized funding requirements and pure capital redeployment for the benefit investors.
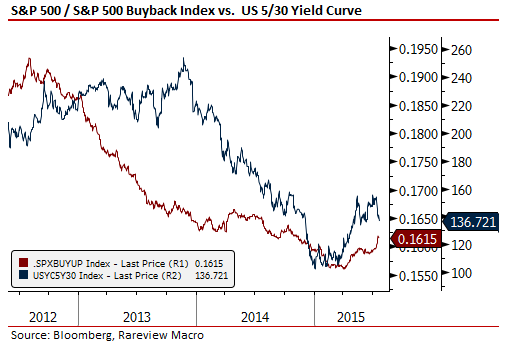
By the way, as we have pointed out in these pages for a while now, not only is the IG spread widening, signaling the distinction noted above, but the equity markets are now doing so as well. Again, see the below chart of the ratio of the S&P 500 to the S&P 500 BUYUP index overlaid with the US Treasury 5-30yr yield curve. Stock buy-backs are simply underperforming in 2015 after multiple years of outperformance as the yield curve steepens in anticipation that interest rate hikes will slow the capital redeployment process down. As a reminder, it is much easier to slow a buy-back than reduce a dividend as the former has a time-band and discretion to implement and the latter generally is a board-level decision.
 Secondly, we are aware that discussions around the lack of liquidity in the credit markets are a near daily occurrence these days. The only observation of note is that there is now a new term associated with the market construct – that is, “liquidity cost basis”. In simple terms, due to the lack of market depth and the continued sensational appetite to issue bonds, there is now a higher premium being applied in the market to finding liquidity if you want to own a bond. All we are saying is that the investor concerns over liquidity are not only being priced into the market but those worries have been crystalized with a fancy Wall Street name.
Secondly, we are aware that discussions around the lack of liquidity in the credit markets are a near daily occurrence these days. The only observation of note is that there is now a new term associated with the market construct – that is, “liquidity cost basis”. In simple terms, due to the lack of market depth and the continued sensational appetite to issue bonds, there is now a higher premium being applied in the market to finding liquidity if you want to own a bond. All we are saying is that the investor concerns over liquidity are not only being priced into the market but those worries have been crystalized with a fancy Wall Street name.
The end result is that investors are demanding a higher premium for the new issues they are taking down, largely due to deteriorating fundamentals in the actual credit.
Now, the second most widely cited explanation for the spread widening is that it is due to the energy sector. If you decompose the spreads it is easier to argue that a notable portion of the weakness is due to the deterioration in the energy sector, whose credit spreads are highly correlated with the lower price of crude oil. However, energy makes up a much smaller portion of the investment grade market (~12%) than it does for the high yield (i.e. ~18%+), which indicates that the breadth of weakness stretches across many other sectors of the investment grade market and is not due to one single risk factor, such as crude oil.
Lastly, we would note that the absolute levels of these spreads referenced on the chart above are also consistent with weakness after the US quantitative easing program was completed and in anticipation of an interest rate hike. We are not sure how much of the spread widening is a result of this less easy monetary policy but the fact is that both QE and the zero interest rate policy forced investors to perpetually search for yield and investment grade credit was a major source of that appetite. To what degree that happened is difficult to handicap but some of those inflows have to reverse given how asymmetric the outcome would be if the Federal Reserve actually embarked on a rate hiking cycle consistent with past cycles, as opposed to a gradual pace of hikes.
Taking a step back, if you look at both the US yield curve and the credit markets, what you find is that both are saying roughly the same thing – that is, there is currently a recession risk embedded in the market, and that there is the potential for the end of this credit and/or economic cycle to be on the horizon.
Take what we have just sketched out any way you want. We are not making a bearish call on risk assets or attempting to sell blood. All we are doing is saying that credit markets, the yield curve and corporate share repurchase trends are signaling some concern sometime over the next 6-9 months. Given that we have not had a recession in 6-7 years, and historically we have had one every four years on average in the modern era, it is not at all unreasonable to start to watch these signals a lot more closely from now on for something more acute.
Above segment from investment newsletter Sight Beyond Sight is re-published with permission from global macro think tank Rareview Macro LLC. Subscription to the daily commentary and trade strategy profiles is available via the firm’s website